The treatment landscape for narcolepsy-related sleepiness has expanded beyond traditional stimulants. Two notable newer options are Solriamfetol and Pitolisant:
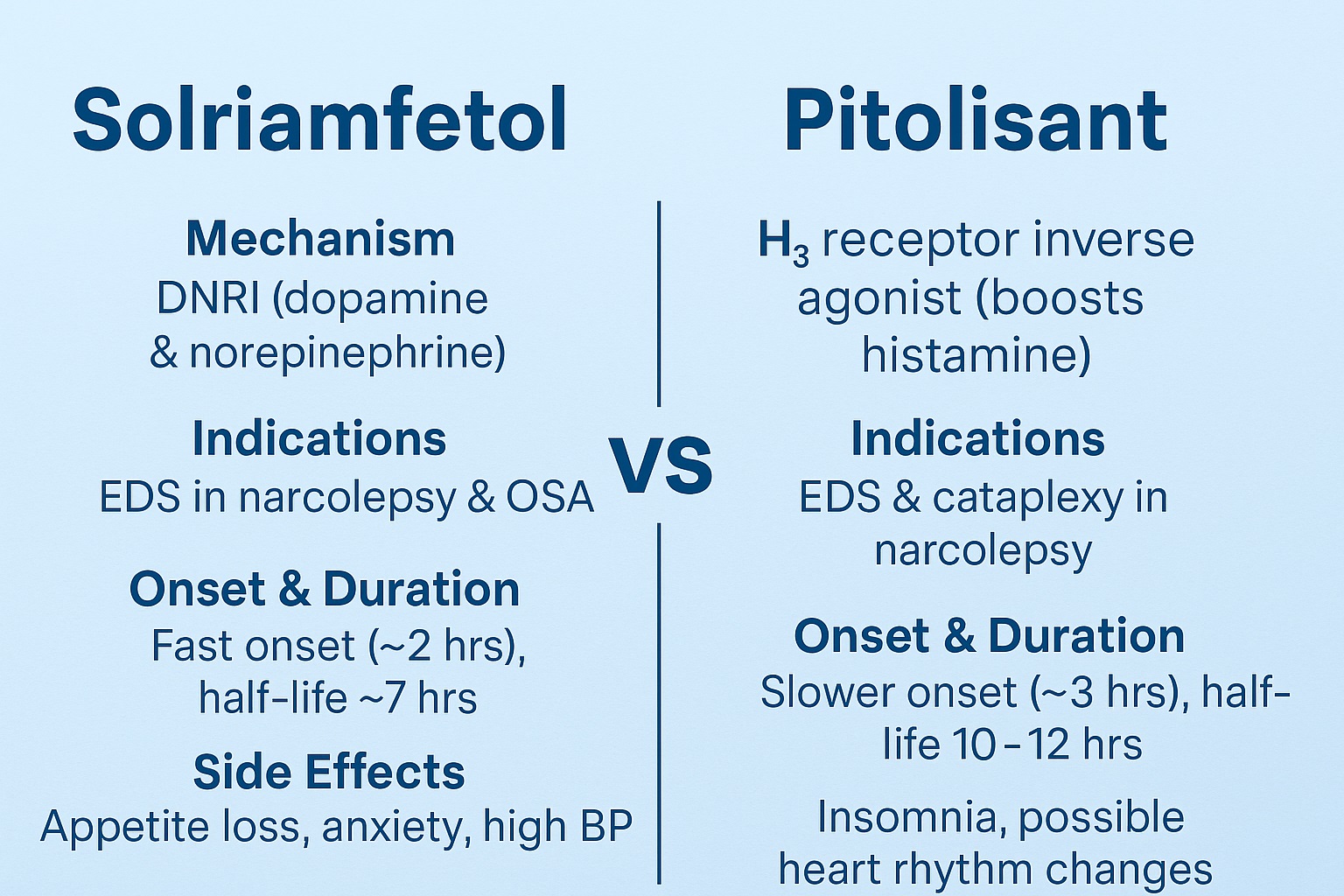
- Solriamfetol (brand name Sunosi) — a dopamine-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (DNRI)
- Pitolisant (brand name Wakix) — a histamine H₃ receptor inverse agonist
Though both promote wakefulness, their mechanisms, regulatory status, side effect profiles, and cost-effectiveness vary significantly.
Mechanisms of Action
- Solriamfetol works by blocking reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, increasing concentration of these wakefulness-promoting neurotransmitters. Studies also suggest activity at trace amine receptor TAAR1 adds to its effect.
- Pitolisant modulates the brain’s histamine system by acting as an inverse agonist at H₃ receptors, enhancing histaminergic activity to promote alertness without typical stimulant mechanisms.
Approved Uses & Regulatory Insights
- Solriamfetol is approved for narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)-related EDS. It shows effectiveness particularly in OSA patients who need more wakefulness support.
- Pitolisant is approved for narcolepsy (with or without cataplexy) and has shown effectiveness in improving both EDS and cataplexy symptoms.
Safety Profiles & Side Effects
- Solriamfetol side effects include headache, nausea, decreased appetite, insomnia, anxiety, and potential cardiovascular effects such as increased heart rate and blood pressure .
- Pitolisant tends to have a better safety profile, particularly for those with cardiovascular concerns. Its common side effects include insomnia, headache, nausea, and anxiety; rare but serious risks include increased heart rhythm abnormalities.
Efficacy & Cost-Effectiveness
- Solriamfetol has demonstrated strong efficacy for EDS, and NICE guidelines suggest it may be more cost-effective than pitolisant, especially when other first-line treatments fail .
- Pitolisant, though not always the most economical, is prized for its non-controlled status in some regions (e.g., the U.S.) and its ability to address cataplexy more directly
Final Comparison Table
| Feature | Solriamfetol (Sunosi) | Pitolisant (Wakix) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | DNRI (dopamine & norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor) | H₃ receptor inverse agonist (boosts histamine) |
| Indications | EDS in narcolepsy & OSA | EDS & cataplexy in narcolepsy |
| Onset & Duration | Fast onset (~2 hrs), half-life ~7 hrs | Slower onset (~3 hrs), half-life 10–12 hrs |
| Side Effects | Appetite loss, anxiety, high BP/HR | Insomnia, possible heart rhythm changes |
| Safety Profile | Less favorable for CV risk patients | Better CV safety; non-controlled in US |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Considered more cost-effective by NICE | More expensive but helps with cataplexy |
When to Choose Which?
Choose Solriamfetol if:
- You primarily suffer from EDS due to narcolepsy or OSA.
- You require rapid, sustained alertness.
- Cost or cardiovascular considerations are key.
Choose Pitolisant if:
- Cataplexy is a prominent symptom alongside EDS.
- You prefer a non-amphetamine pathway with lower CV risk.
- You’re concerned about controlled substance restrictions or abuse potential.
Resume:
While both solriamfetol and pitolisant represent meaningful advances in narcolepsy treatment, they serve slightly different clinical niches—one offering powerful dopamine-related wakefulness, the other enhancing histaminergic signaling with lower abuse potential and cataplexy control.